Incretin effect in Type 2 diabetes
What is the incretin effect?
Integrated insulin secretion rates calculated from peripheral venous C-peptide measurements by two-compartment kinetic analysis were measured in six young normal subjects after increasing oral glucose loads of 25, 50, and 100 g and respective isoglycemic glucose infusions. The differences in β-cell secretory responses between oral and iv glucose challenges were attributed to factors other than glycemia itself (incretin effect) [2].
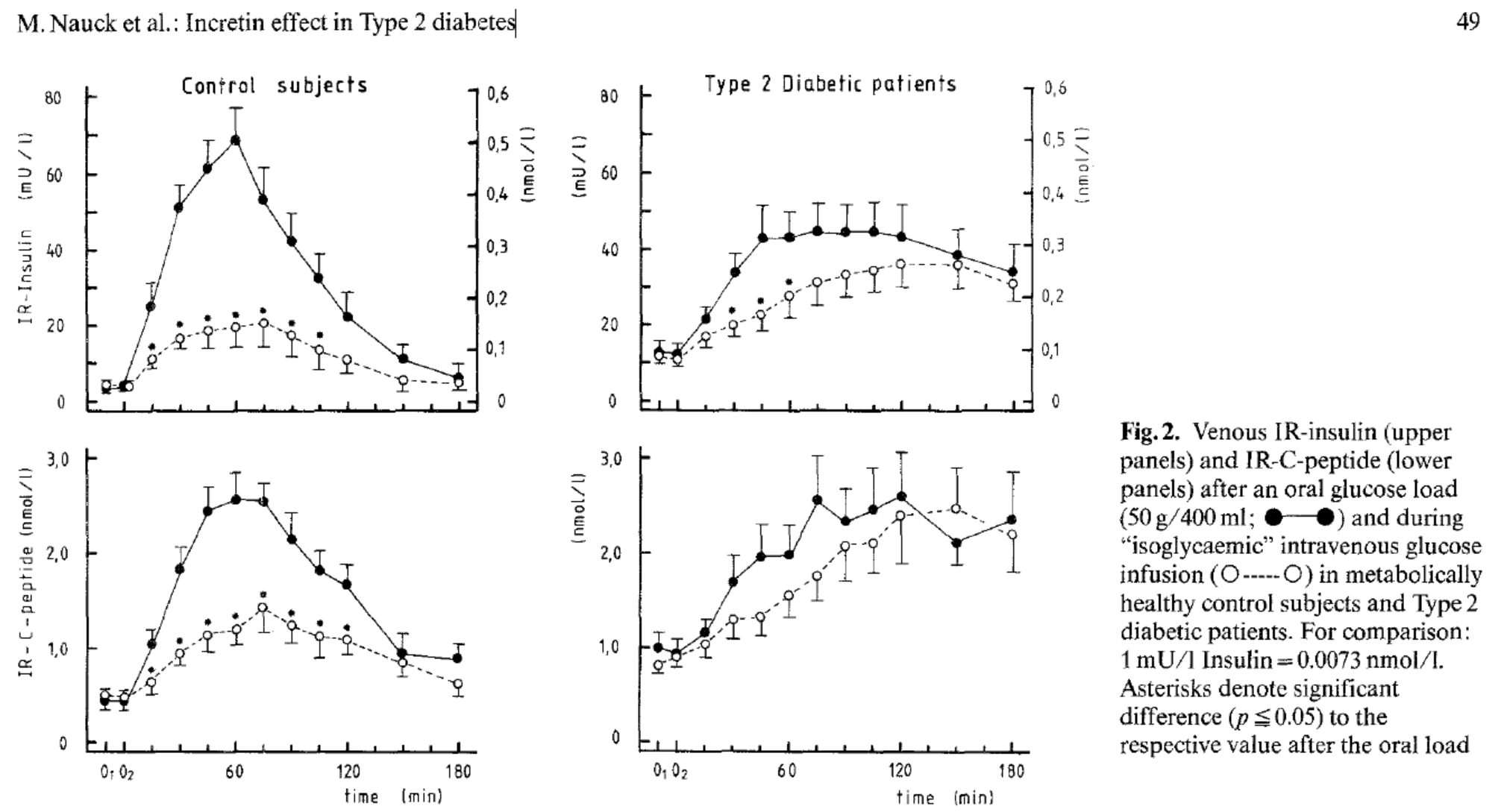
Integrated incremental immunoreactive insulin and connecting peptide responses to an oral glucose load of 50 g
and an "isoglycaemic" intravenous glucose infusion, respectively, were measured in 14 Type 2 (non-insulin-dependent) diabetic patients and 8 age- and weight-matched metabolically healthy control subjects. Differences between responses to oral and intravenous glucose administration are attributed to factors other than glucose itself (incretin effect) [3].
Contact Us
Follow us
 Wechat
Wechat

