UACR
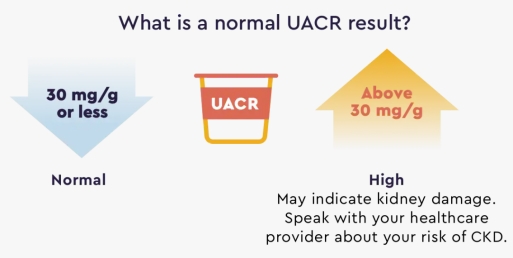
Urinary ACR Chemiluminescent Immunoassay ☑️ Description The urine albumin-creatinine ratio (uACR) shows whether you have albumin in your urine. Albumin is a type of protein that's normally found in the blood. Your body needs protein. It's an important nutrient that helps build muscle, repair tissue, and fight infection. But it should be in your blood, not your urine. When you have albumin (protein) in your urine, it is called albuminuria or proteinuria. One of the main jobs of your kidneys is to filter your blood. Your kidneys keep important things your body needs inside your blood, like protein. They also remove things your body doesn't need, like wastes and extra water. If kidneys are healthy, they should let only very little protein go into your urine – or even none. But if your kidneys are damaged, protein can "leak" out of the kidneys into your urine. People with a high amount of albumin in their urine are at an increased risk of having chronic kidney disease progress to kidney failure. ☑️ UACR urine test An early way to find out if you may have chronic kidney disease (CKD) is by taking a UACR (urine albumin-to-creatinine ratio) test once a year. A UACR test can detect how much small protein, called albumin, is in your urine, which is one of the earliest indicators of CKD or kidney damage. A damaged kidney can’t filter as well as it should and lets some protein pass into the urine. A healthy kidney doesn’t let any protein pass into the urine. A normal amount of albumin in your urine is less than 30 mg/g. Anything above 30 mg/g may mean you have kidney disease. 

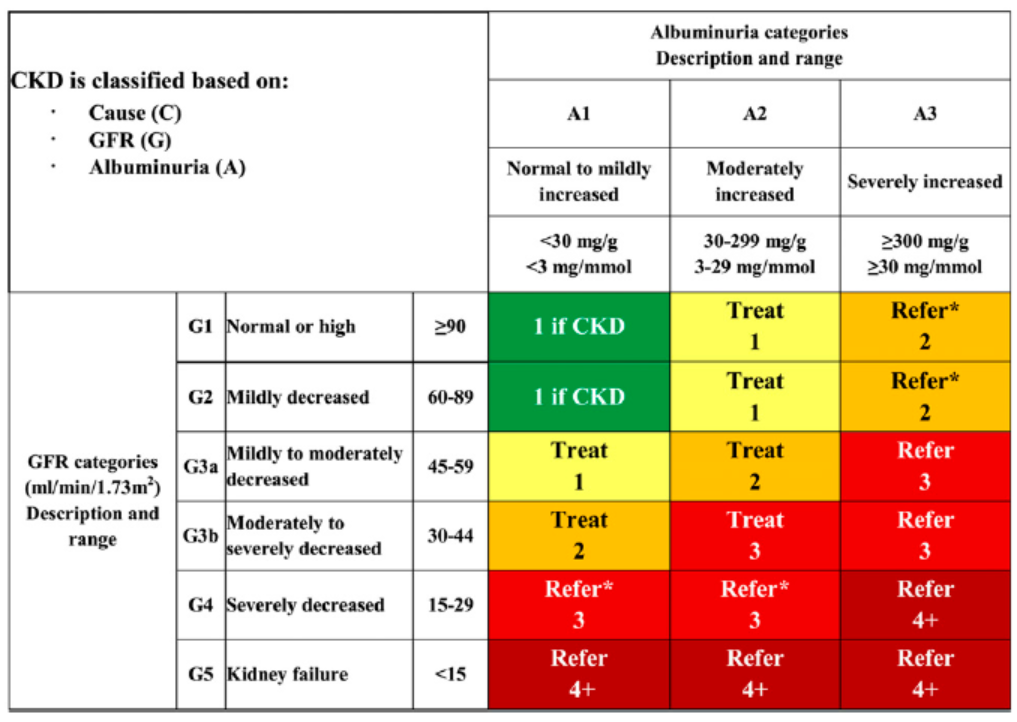
Guideline for the prevention and treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus in China (2020 edition, Clinical guideline for the prevention and treatment of diabetic kidney disease in China (2021edition).
Screening for albuminuria can be most asily performed by urinary albumin-tocreatinine ratio (UACR) in a random spot urine collection.
Contact Us
Follow us
 Wechat
Wechat

